What Is The Maximum Hard Drive Size Allowed When Using The Mbr Partitioning Method?
This browser is no longer supported.
Upgrade to Microsoft Edge to take advantage of the latest features, security updates, and technical support.
Windows back up for hard disks that are larger than 2 TB
This article discusses the manner in which Windows supports hard disks that have a storage chapters of more than two TB and explains how to initialize and division disks to maximize space usage.
Applies to: Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012 R2
Original KB number: 2581408
Summary
In order for an operating system to fully support storage devices that have capacities that exceed 2 terabytes (2 TB, or 2 trillion bytes), the device must exist initialized by using the GUID Partition Table (GPT) division scheme. This scheme supports addressing of the total range of storage capacity. If the user intends to first the computer from one of these large disks, the system'southward base firmware interface must employ the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) and not BIOS.
This article outlines Microsoft support beyond all Windows versions since Windows XP. It also describes the requirements to address the full storage capability of these devices.
Note
- This commodity refers to disk chapters in powers of ii instead of powers of x, which is the more mutual designation on storage device capacity labels. Therefore, references to 2 TB actually refer to a production that is labeled equally having ii.2 TB of chapters.
- The operating system-specific behavior that is noted in this article also applies to the server variants of that organization. Therefore, a reference to Windows vii includes Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Vista includes Windows Server 2008, and Windows XP includes Windows Server 2003 and Windows Server 2003 R2.
More than information
The direction of modern storage devices is addressed past using a scheme called Logical Block Addressing (LBA). Information technology's the arrangement of the logical sectors that found the media. LBA0 represents the first logical sector of the device, and the terminal LBA designation represents the last logical sector of the device, one characterization per sector. To decide the capacity of the storage device, you multiply the number of logical sectors inside the device by the size of each logical sector. The current size standard is 512 bytes. For example, to achieve a device that has a capacity of 2 TB, you must have 3,906,250,000 512-byte sectors. Notwithstanding, a reckoner system requires 32 $.25 (1 s and 0 s) of data to stand for this big number. Therefore, any storage capacity that is greater than what tin be represented by using 32 bits would require an additional bit. That is, 33 bits.
The problem in this ciphering is that the sectionalization scheme that is used past most modern Windows-based computers is MBR (master kick record). This scheme sets a limit of 32 for the number of $.25 that are available to represent the number of logical sectors.
The 2-TB barrier is the result of this 32-bit limitation. Because the maximum number that can exist represented by using 32 bits is 4,294,967,295, it translates to 2.199 TB of capacity by using 512-byte sectors (approximately 2.two TB). Therefore, a capacity beyond 2.2 TB isn't addressable by using the MBR sectionalisation scheme.
To brand more $.25 available for addressing, the storage device must exist initialized by using GPT. This sectionalization scheme lets upward to 64 $.25 of information be used within logical sectors. It translates to a theoretical limitation of 9.4 ZB (9.4 zettabytes, or 9.4 billion terabytes). However, the issue that affects GPT is that about currently available systems are based on the aging BIOS platform. BIOS supports only MBR-initialized disks to start the reckoner. To restart from a device that is initialized by using GPT, your organization must be UEFI-capable. By default, many electric current systems can support UEFI. Microsoft expects that most future systems will take this support. Customers should consult with their arrangement vendor to determine the ability of their systems to support UEFI and disks that take storage capacities that are greater than ii TB.
Overall requirements for a non-bootable data book
For a organisation to be able to accost the maximum chapters of a device that has a storage capacity of more than two TB, the following prerequisites apply:
-
The deejay must be initialized by using GPT.
-
The Windows version must exist 1 of the following (32-chip or 64-fleck, unless otherwise noted, but including all SKU editions):
- Windows Server 2008 R2 (only 64-bit version bachelor)
- Windows Server 2008
- Windows seven
- Windows Vista
-
The latest storage drivers from your storage controller manufacturer must be installed. For example, if your organisation uses an Intel storage controller that is set to "RAID" mode, brand sure that you lot take the latest applicative drivers from the Intel back up site.
-
Overall, you should contact your system vendor to determine whether the system supports device sizes of more than 2 TB.
Overall requirements for a bootable arrangement volume
Assume that you lot want to meet the post-obit conditions:
- Have a storage device on which you tin install Windows.
- Make the storage device bootable.
- Enable the operating system to accost a maximum storage capacity for that device of greater than 2 TB.
To meet these weather condition, the following prerequisites apply:
-
The disk must exist initialized by using GPT.
-
The system firmware must utilize UEFI.
-
The Windows version must be one of the following (64-bit only, but including all SKU editions):
- Windows Server 2008 R2
- Windows Server 2008
- Windows 7
- Windows Vista
-
The latest storage drivers from your storage controller manufacturer must be installed. For example, if your system uses an Intel storage controller gear up to RAID fashion, brand certain that you lot have the latest applicative drivers from the Intel back up site.
Note
Windows does not support starting GPT-initialized volumes by using UEFI systems on 32-bit versions of Windows. Also, legacy BIOS systems practice not support starting GPT-partitioned volumes. Consult your system vendor to decide whether the system supports both UEFI and the startup of devices that have storage capacities of greater than ii TB.
Support matrix
The post-obit tables listing Microsoft support for the various concepts that are discussed in this article. This information provides an overall support argument most disks that have a storage capacity of greater than two TB.
Table 1: Windows support for partitioning schemes as information volumes
| Organisation | MBR | Hybrid-MBR | GPT |
|---|---|---|---|
| Windows 7 | Supported | Not Supported | Supported |
| Windows Vista | Supported | Non Supported | Supported |
| Windows XP | Supported | Not Supported | Not Supported |
Hybrid-MBR is an alternative fashion of partitioning that isn't supported by whatever version of Windows.
Table two: Windows support for system firmware
| System | BIOS | UEFI |
|---|---|---|
| Windows vii | Supported | Supported |
| Windows Vista | Supported | Supported |
| Windows XP | Supported | Non Supported |
Table 3: Windows support for combinations of boot firmware and sectionalization schemes for the kicking volume
| System | BIOS + MBR | UEFI + GPT | BIOS + GPT | UEFI + MBR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows seven | Supported | Supported; requires a 64-bit version of Windows | Boot volume not supported | Kick volume not supported |
| Windows Vista | Supported | Supported; requires a 64-bit version of Windows | Boot volume non supported | Boot volume not supported |
| Windows XP | Supported | Not supported | Boot volume not supported | Kick volume not supported |
Table four: Windows support for big-capacity disks every bit non-booting data volumes
| System | >two-TB single disk - MBR | >2-TB single deejay - Hybrid-MBR | >two-TB single disk - GPT |
|---|---|---|---|
| Windows 7 | Supports up to 2 TB of addressable capacity** | Non Supported | Supports full capacity |
| Windows Vista | Supports up to ii TB of addressable chapters** | Not Supported | Supports full capacity |
| Windows XP | Supports up to 2 TB of addressable capacity** | Not Supported | Non Supported |
Capacity across 2 TB cannot be addressed by Windows if the disk is initialized by using the MBR segmentation scheme. For instance, for a 3-TB unmarried disk that is initialized past using MBR, Windows can create partitions upward to the offset ii TB. However, the remaining capacity cannot be addressed and, therefore, cannot be used.
Initialize a information disk by using GPT
The post-obit steps testify how to initialize a fresh deejay by using the GPT segmentation scheme to help ensure that Windows can address the maximum available storage capacity. Make sure that y'all back up any important data earlier you endeavor these steps.
-
Click Beginning, type diskmgmt.msc in the Start search box, correct-click diskmgmt.msc, and so click Run as Ambassador. If information technology's necessary, enter the credentials for a user account that has Ambassador privileges.
Note
When a non-initialized disk is detected by Windows, the post-obit window opens to prompt yous to initialize the disk.
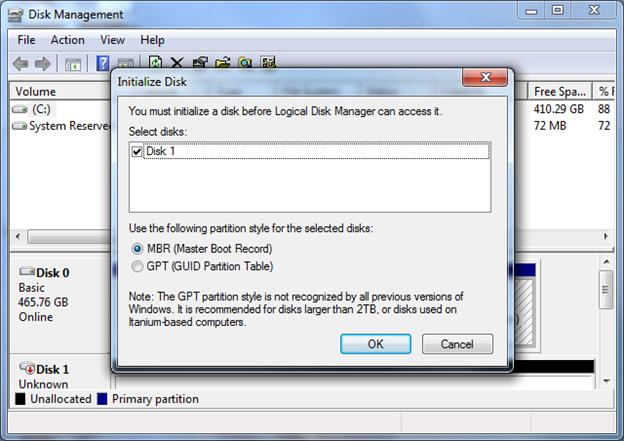
-
In the Initialize Deejay dialog box, click GPT (GUID Partition Tabular array), and and then printing OK.
Note
If you select this selection, this hard disk drive will non be recognized by Windows versions earlier than and including Windows XP.
-
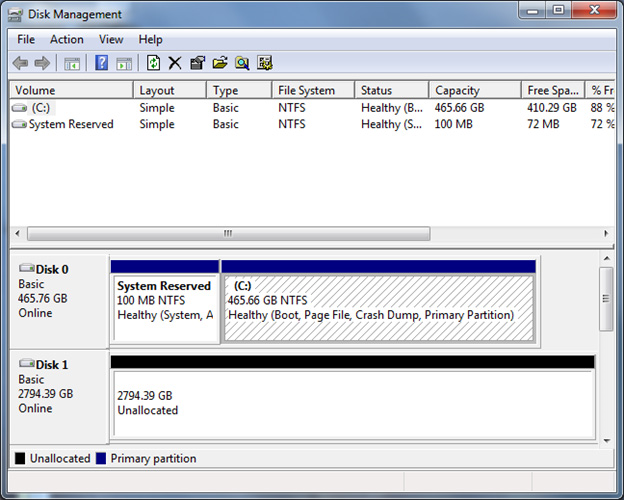
Cheque the Deejay Management window to verify that the disk is initialized. If it is, the status row for that disk at the bottom of the window should indicate that the deejay is Online.
-
After the disk is initialized, you must create a partition, and then format that partition by using a file system. It'south to be able to shop data in that partition, and assign a name and a bulldoze letter to that partition. To do information technology, right-click the unallocated infinite on the right side of the status row for that disk, and then click New Simple Volume. Follow the steps in the sectionalization magician to complete this process.
Convert an MBR deejay to GPT
If you have previously initialized the disk by using the MBR partitioning scheme, follow these steps to initialize the disk by using the GPT scheme. Brand certain that you back up any important data before yous try these steps.
-
Click Start, type diskmgmt.msc in the Start search box, right-click diskmgmt.msc, and so click Run as Administrator. If it's necessary, enter the credentials for a user account that has Ambassador privileges.
-
In the Disk Management window, examine the disk status rows at the bottom. In the following instance, the user has a 3-TB disk that was previously initialized by using the MBR partitioning scheme. That device is labeled here as Disk one.
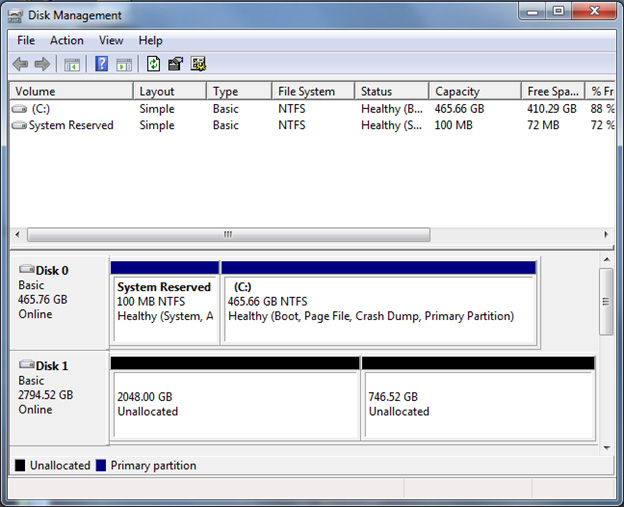
-
Disk 1 contains 2 separate unallocated sections. This separation indicates that the commencement 2 TB of the deejay space can be used. Yet, the remaining space is non-addressable because of the 32-bit addressing space limitation of the MBR segmentation scheme. To enable the organisation to fully address the total capacity of the storage device, you lot must convert the disk to utilise the GPT partitioning scheme.
-
Correct-click the label on the left for the deejay that you want to convert, and then click Convert to GPT Disk.
Note
The display should now bear witness that the full corporeality of available space in unallocated.
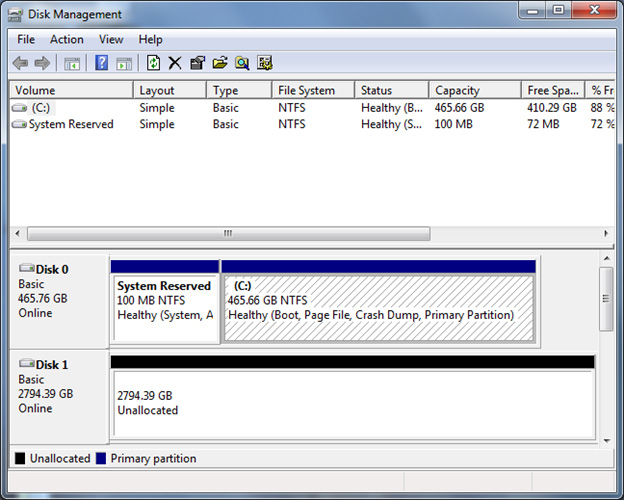
-
Now that the deejay is initialized to access the full storage chapters, you must create a segmentation, and then format that partition by using a file system. It's to be able to store data in that partition, and assign a name and a bulldoze letter to that sectionalisation. To do information technology, right-click the unallocated space on the right side of the status row for that deejay, and so click New Simple Volume. Follow the steps in the partition wizard to complete this process.
Known issues or limitations
Because the transition to a single-disk capacity of greater than 2 TB has occurred fairly recently, Microsoft has investigated how Windows supports these big disks. The results reveal several bug that utilise to all versions of Windows earlier than and including Windows seven with Service Pack 1 and Windows Server 2008 R2 with Service Pack 1.
To this indicate, the following incorrect behavior is known to occur when Windows handles unmarried-disk storage capacity of greater than ii TB:
-
The numeric chapters across 2 TB overflows. It results in the system being able to address only the capacity across 2 TB. For example, on a 3-TB disk, the available capacity may exist only 1 TB.
-
The numeric capacity beyond two TB is truncated. It results in no more than 2 TB of addressable infinite. For case, on a 3-TB disk, the bachelor chapters may be only 2 TB.
-
The storage device isn't detected correctly. In this case, it isn't displayed in either the Device Managing director or Disk Management windows. Many storage controller manufacturers offer updated drivers that provide support for storage capacities of more than 2 TB. Contact your storage controller manufacturer or OEM to make up one's mind what downloadable support is bachelor for unmarried-disk capacities that are greater than two TB.
SCSI sense data
When a deejay encounters errors that are related to unreadable or unwritable sectors, information technology reports those errors and the relevant SCSI sense information to the operating system. SCSI sense data may contain information about LBA for sectors that were found to exist unreadable or unwritable.
For LBA address space that is greater than 2 TB, the disk requires SCSI sense data in Descriptor format. This format isn't supported by Windows 7 or Windows Server 2008 R2, which retrieves SCSI sense data in Fixed format. Therefore, the retrieved SCSI sense information either does not contain information most bad sectors or information technology contains incorrect information near bad sectors. Administrators should note this limitation when they look for bad sector LBA information that's recorded in the Windows event log.
What Is The Maximum Hard Drive Size Allowed When Using The Mbr Partitioning Method?,
Source: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/troubleshoot/windows-server/backup-and-storage/support-for-hard-disks-exceeding-2-tb
Posted by: tallenthinst1998.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Is The Maximum Hard Drive Size Allowed When Using The Mbr Partitioning Method?"
Post a Comment